For java_intermediate course. https://giangtester.com/khoa-hoc-java-intermediate/
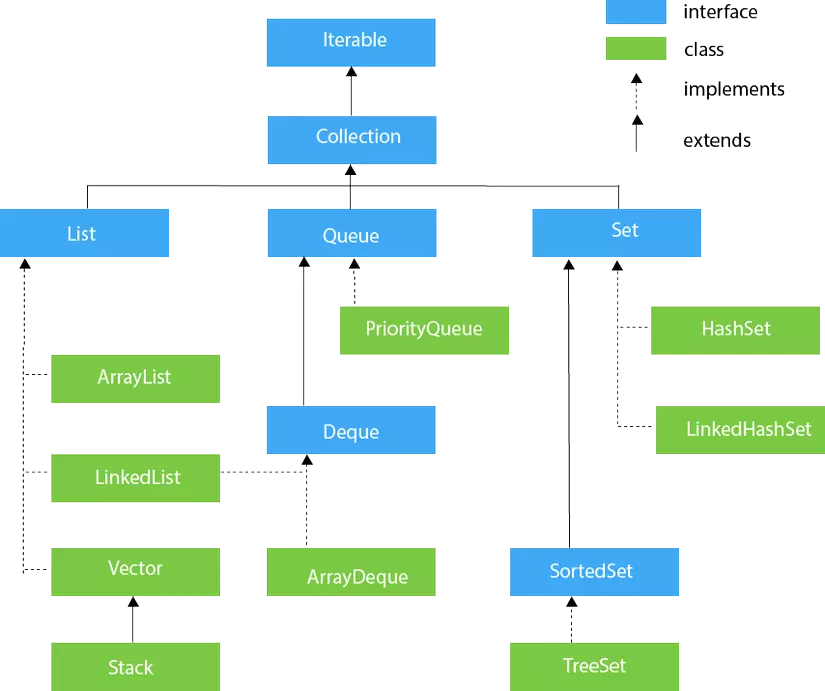
I. Collection
- is a “bag” = unordered lists
- No direct implementation
Collection<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
- Add one element
names.add("john");
System.out.println(names); //[john]
- Add multiple elements
names.addAll(List.of("james, harry"));
System.out.println(names); //[james, harry]
-----------------------------------------
Collection<String> names = new ArrayList<>(List.of("john", "james", "harry"));
- Remove one element
names.remove("john");
System.out.println(names); //[james, harry]
- Remove multiple elements
names.removeAll(List.of("james", "harry"));
System.out.println(names); //[john]
- Remove based on a condition
names.removeIf(s -> s.startsWith("j"));
System.out.println(names); //[harry]
- Remove all elements
names.clear();
System.out.println(names); //[]
- Remove the differences
Collection<String> names2 = new ArrayList<>(List.of("john", "james", "Steve"));
names.retainAll(names2);
System.out.println(names); //[john, james]
-----------------------------------------
Collection<String> names = new ArrayList<>(List.of("john", "james", "harry"));
- Print each element
names.forEach(System.out::println); //john james harry
- Get size
System.out.println(names.size()); //3
- Check empty
System.out.println(names.isEmpty()); //false
- Check contain one element
System.out.println(names.contains("harry")); //true
- Check contain multiple elements
System.out.println(names.containsAll(List.of("harry", "john"))); //true
-----------------------------------------
Collection<String> names = new ArrayList<>(List.of("john", "james", "harry"));
- Convert to array with array type
String[] strings = names.toArray(new String[]{});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strings)); //[john, james, harry]II. List
- A collection in which order is significant
- Allow duplicate elements
- Insert and get element fast → ArrayList
- Insert and remove fast → LinkedList
- When need multi-thread → CopyOnWriteArrayList
Methods
List contains all methods that defines in collection interface, and some methods work with index.
List<String> chars = new ArrayList<>(List.of("a", "b", "c"));
- Add an element at position
chars.add(2, "new");
System.out.println(chars); //[a, b, new, c]
- Add multiple elements at position
chars.addAll(2, List.of("newA", "newB"));
System.out.println(chars); //[a, b, newA, newB, c]
- Edit an element at position
chars.set(2, "newA");
System.out.println(chars); //[a, b, newA]
- Get an element at position
System.out.println(chars.get(0)); //a
- Check index of an element
System.out.println(chars.indexOf("b")); //1
- Remove an element at position
chars.remove(1);
System.out.println(chars); //[a, c]
-------------------------------------------------
- Create an unmodified list
List<String> chars = List.of("a", "b", "c");
- Create list from an unmodified list
List<String> chars = new ArrayList<>(List.of("a", "b", "c"));
- Sort a list a --> z
List<String> chars = new ArrayList<>(List.of("b", "a", "c"));
chars.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder());
System.out.println(chars); //[a, b, c]
- Sort a list z --> a
chars.sort(Comparator.reverseOrder());
System.out.println(chars); //[c, b, a]
- Replace/Update all elements
List<String> chars = new ArrayList<>(List.of("a", "b", "c"));
chars.replaceAll(s -> s + "_1");
System.out.println(chars); //[a_1, b_1, c_1]III. Set
- No duplicates
- Order is not significant
- No more methods than Collection interface
- Don’t care order → HashSet
- Keep insertion order → LinkedHashSet
- Store Enum in a Set → EnumSet
- When need multi-thread, size small, read more – less write → CopyOnWriteArraySet
- Auto sort element → TreeSet
- When need multi-thread + Auto sort → ConcurrentSkipListSet
Methods
- Create a set
Set<String> uniqueNames = new HashSet<>();
- Create an unmodified set
Set<String> uniqueNames = Set.of("b", "a", "c");
System.out.println(uniqueNames); //[a, b, c]
- Create a set from a list
Set<String> uniqueNames = new HashSet<>(List.of("a", "b", "a", "c"));
System.out.println(uniqueNames); //[a, b, c]IV. Map
- key-value associations to store and retrieve elements
- Normal map → HashMap
- Keep insertion order → LinkedHashMap
- Key is Enum → EnumMap
- Auto sort → TreeMap
- When multi-thread → ConcurrentHashMap
Methods
- Create an normal map
Map<Integer, String> names = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Person> names = new HashMap<>();
- Create an unmodified map
Map<Integer, String> names = Map.of(1, "john", 2, "james");
- Create a modified map from an unmodified map
Map<Integer, String> names = new HashMap<>(Map.of(1, "john", 2, "james"));
---------------------------------------
Map<Integer, String> names = new HashMap<>();
- Add one element
names.put(1, "john");
System.out.println(names); //{1=john}
- Add multiple elements
names.putAll(Map.of(1, "john", 2, "james"));
System.out.println(names); //{1=john, 2=james}
- Get value by key
String name = names.get(1);
System.out.println(name); //john
- Get value by key, if don't exist return default value
String name = names.getOrDefault(3, "NOT_FOUND");
System.out.println(name); //NOT_FOUND
---------------------------------------
Map<Integer, String> names = new HashMap<>(Map.of(1, "john", 2, "james"));
- Get all keys
Set<Integer> keys = names.keySet();
System.out.println(keys); //[1, 2]
- Get all values
Collection<String> values = names.values();
System.out.println(values); //[john, james]
- Print key-value
names.forEach((k, v) -> System.out.printf("k=%s, v=%s %n", k, v));
//k=1, v=john
//k=2, v=james
---------------------------------------
- Update multiple values
Map<Integer, String> names = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
names.compute(i, (k, v) -> "john_" + k);
}
System.out.println(names); // {0=john_0, 1=john_1, 2=john_2, 3=john_3}